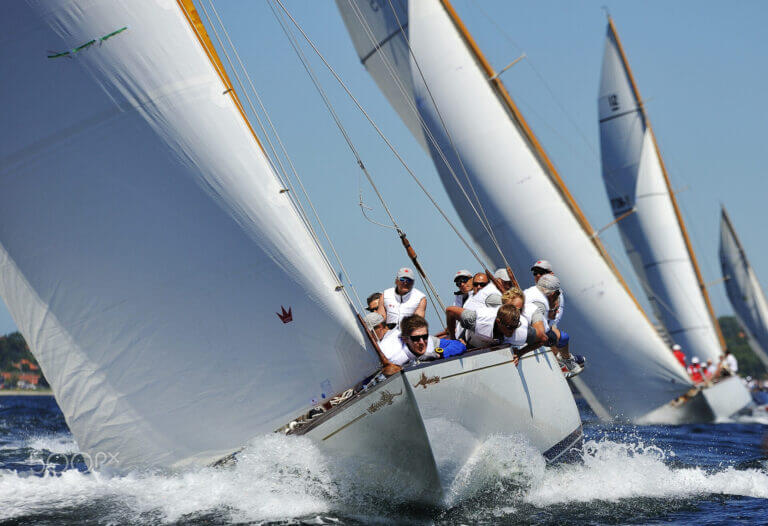
What is a Sloop? Definition, Types and History
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig.
Sloops are a type of sailboat that has been around for centuries. They are known for their versatility and ease of handling, making them popular among sailors of all skill levels. Sloops have a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig that allows for efficient sailing in a variety of wind conditions, making them an excellent choice for both cruising and racing.
Sloops are designed to be easy to handle, even for novice sailors. The simple rigging system means that there are fewer lines to manage than on other types of sailboats, which makes it easier to focus on sailing the boat. This simplicity also means that sloops require less maintenance than other boats, which can save you time and money in the long run.
One of the great things about sloops is how versatile they are. They can be used for everything from day sailing to long-distance cruising to racing. Their design allows them to sail efficiently in a wide range of wind conditions, from light breezes to strong winds. This versatility makes them an excellent choice for sailors who want a boat that can do it all.
The Versatile and Popular Sloop Sailboat Rig
Single Mast and Fore-and-Aft Rig
A sloop is a type of sailboat that has a single mast and a fore-and-aft rig. This means that the sails are positioned parallel to the length of the boat, making it easier for sailors to control the direction of the boat. The simplicity and versatility of the sloop rig make it one of the most popular sailboat rigs in use today.
Mainsail and Headsail
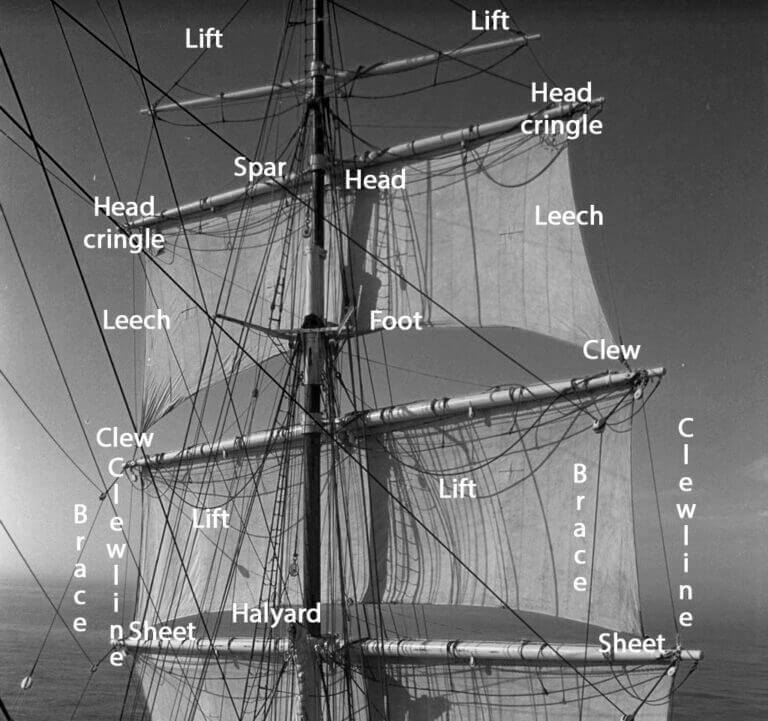
The mainsail is the largest sail on a sloop, and it is attached to the mast and boom. It provides power to move the boat forward. The headsail, which is also known as a jib or genoa, is attached to the forestay and helps to control the boat’s direction by creating lift. Together, these two sails work together to provide speed and maneuverability.
Crew Size
A sloop is typically crewed by one or two sailors, although larger sloops may require more crew members to handle the sails and other equipment. The size of a sloop can vary greatly, from small dinghies used for recreational sailing to large ocean-going vessels used for racing or long-distance cruising.
Variations of Sloops
Bermuda-Rigged Sloop
The Bermuda-rigged sloop is a classic design that has been around for centuries. It features a mainsail and a jib, which is a type of headsail. This design is popular among sailors because it is easy to handle and provides good performance in a wide range of wind conditions.

One of the advantages of the Bermuda rig is that it allows for more headsails to be used than other types of rigs, such as ketches or schooners. This means that sailors can adjust their sails to match changing wind conditions, giving them greater control over their sailing vessel.
Another advantage of the Bermuda rig is its simplicity. The sail plan is relatively easy to set up and maintain, making it an ideal choice for beginners or those who prefer a minimalist approach to sailing.
Gunter-Rigged Sloop
The Gunter-rigged sloop is another traditional design that has been around for centuries. It features a mainsail and a jib, but instead of using a masthead rig like the Bermuda sloop, it uses a gaff rigged mast with an additional spar called the gaff topsail.
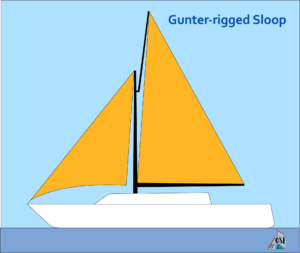
This design was popular in the 19th century because it allowed sailors to carry more sail area without having to use taller masts. However, it fell out of favor in the early 20th century when newer designs were developed that provided better performance.
Despite this, there are still some sailors who prefer the Gunter rig because of its traditional look and feel. It can also be easier to handle than some other types of rigs because the sails are smaller and lighter.
Gaff-Rigged Sloop
The gaff-rigged sloop is similar to the Gunter rig in that it uses a gaff rigged mast with an additional spar called the gaff topsail. However, it also features a headsail like the Bermuda rig.

In the past, boats commonly used gaff rigged sails, but now they have mostly been replaced by Bermuda rig sails. These newer sails are simpler than the gaff rig and allow boats to sail closer to the wind.
Spritsail Sloop
The spritsail sloop is one of the simplest rigs available. It features a single sail called the spritsail, which is attached to a spar called the sprit. This design was popular among fishermen and other working boats because it was easy to set up and maintain.

Although not as popular as before, some sailors still prefer the simplicity of a spritsail rig. It’s a great option for those who want to focus on sailing without the added complexity of multiple lines or sail plans. This type of rig is also suitable for beginner sailors and those who want an easy-to-handle boat.
The Origin of the Word Sloop
The word “sloop” is believed to have originated from the Dutch word “sloep”, which means a small boat used for fishing or transportation. The Dutch were known for their seafaring skills and had a significant influence on maritime culture in Europe during the 17th century. As such, it’s no surprise that many nautical terms used today have Dutch origins.
In fact, the sloop was initially developed in Holland during the 16th century as a small, single-masted vessel used primarily for fishing and coastal trading. These boats were highly maneuverable and could navigate shallow waters with ease, making them ideal for use in Holland’s many canals and waterways.
As Dutch sailors began to explore further afield, they brought their sloops with them, using them as auxiliary vessels to transport goods and personnel between larger ships and shore. Over time, sloops evolved into larger vessels capable of longer voyages and more extensive cargo capacity.
History of Sloops
Sloops have been a popular type of ship for centuries, with their unique rigging and hull design allowing for greater speed and maneuverability compared to other vessels. Let’s take a closer look at the history of sloops and how they have evolved over time.
17th Century: The Birth of Sloops
Sloops first emerged in the 17th century as small, fast ships used for coastal trading and piracy. Their single mast and fore-and-aft sail plan allowed them to navigate shallow waters with ease, making them ideal for smuggling goods or evading authorities. Despite their reputation as pirate ships, sloops were also used by legitimate traders due to their speed and efficiency.
18th Century: Sloops in War
In the 18th century, sloops became increasingly popular among naval forces due to their speed and agility. The British Royal Navy used sloops as dispatch vessels and reconnaissance ships during times of war. Pirates and privateers also favored sloops due to their ability to outrun larger vessels. As a result, the term “sloop-of-war” was coined to describe a small warship with a single mast and crew of around 75 men.

19th Century: Racing Sloops
The 19th century saw the rise of yacht racing, with sloops becoming a popular choice among sailors due to their versatility and ease of handling. In fact, the first recorded yacht race took place in 1826 between two sloops on the Hudson River. Sloops continued to be used for racing throughout the century, with improvements in rigging and hull design leading to faster vessels.
Modern Times: Versatile Sloops
Today, sloops are still widely used for racing and cruising due to their versatility. They are often chosen by recreational sailors who want an easy-to-handle vessel that can navigate both shallow coastal waters and open seas. Modern sloops come in various sizes, from small day-sailers to larger cruising boats. Some sloops even incorporate multiple masts, such as the ketch rig, which features a smaller mizzen mast behind the main mast.
Advantages of a Sloop
Single Mast: Easier to Handle and Maneuver
Sloops are popular sailboats that have a single mast, which makes them easier to handle and maneuver compared to other sailboat types. The simplicity of the sloop rig means that it requires less maintenance and is generally less expensive to maintain compared to other sailboat types. With only one mast, there are fewer lines and sails to manage, making it easier for sailors who are new to sailing or those who prefer a simpler setup.
The single mast design also allows for better visibility on the water since there is no obstruction from multiple masts or rigging. This feature is especially useful when sailing in crowded waters where you need to keep an eye out for other boats or obstacles.
Faster Sailing and Closer to the Wind
Another advantage of sloops is their speed. Sloops are generally faster than other sailboat types due to their streamlined design with fewer sails. The Bermuda sloop, for example, has a triangular mainsail and one or more headsails, allowing it to move quickly through the water with minimal drag.
Sloops can also sail closer to the wind than most other sailboats. This means they can tack (sail against the wind) more efficiently, allowing them to cover more ground in less time. The ability of a sloop’s sails to be adjusted easily helps in this regard as well.
Wide Variety Available
As the most popular contemporary boat, sloops are available in a wide variety. They come in different sizes and designs suitable for various purposes such as racing, cruising, or day sailing. Some sloops even have additional sails like mizzenmast or more headsails which make them more versatile.
For instance, some sloops have a mizzenmast located aft of the mainmast which provides additional support for larger boats during heavy winds. Other sloops may have multiple headsails that allow them greater flexibility when adjusting to different wind conditions. These additional sails can make a sloop more expensive to maintain, but they also provide greater versatility and options for the sailor.
Disadvantages of a Sloop
Limited Sail Options in Heavy Weather Conditions
Sloops are known for their simplicity and ease of handling, but they have some disadvantages that sailors should be aware of. One of the biggest drawbacks is the limited sail options in heavy weather conditions. Sloops typically have a single forestay that supports the mast, which means that they can only fly one headsail at a time. This can be problematic when sailing upwind in strong winds or heavy seas.
In these conditions, it’s often necessary to reduce sail area to maintain control and prevent damage to the boat or rigging. With a sloop, this usually means taking down the headsail and relying on the mainsail alone. While this can work well in moderate wind conditions, it may not provide enough power or stability in stronger winds.
Difficulty in Handling Larger Sails Alone
Another disadvantage of sloops is that they can be difficult to handle when sailing with larger sails alone. As mentioned earlier, sloops rely on a single forestay to support the mast and headsail. When you increase the size of the sail, you also increase the load on the forestay and rigging.
This means that you may need additional crew members to help manage larger sails safely. If you’re sailing solo or with a small crew, this can make it challenging to get the most out of your boat without putting yourself at risk.
Higher Loads on Mast and Rigging Due to Single Forestay Design
The single forestay design used by sloops also puts higher loads on both the mast and rigging compared to other sailboat designs. The forestay is responsible for supporting not only the headsail but also part of the mast itself.
This means that any stress placed on the headsail or rigging will be transferred directly to the mast through this single point of attachment. Over time, this can lead to fatigue and wear on both the mast and rigging components.

Increased Risk of Broaching in Strong Winds
Sloops are also more prone to broaching in strong winds compared to other sailboat designs. Broaching occurs when a boat is hit by a large wave or gust of wind from the side, causing it to heel over and potentially capsize.
Because sloops have a smaller cockpit and rely on a single forestay for support, they may be more susceptible to this type of event. This can be especially dangerous if you’re sailing in rough conditions or offshore where rescue may not be immediately available.
Reduced Stability Compared to Other Sailboat Designs
Another disadvantage of sloops is that they offer reduced stability compared to other sailboat designs. Sloops typically have a narrower beam and less ballast than other boats of similar size, which can make them feel less stable in heavy seas or choppy water.
This lack of stability can also affect your ability to maintain course and steer accurately, especially when sailing upwind or in challenging conditions. It’s important to understand the limitations of your boat and adjust your sailing style accordingly.
Conclusion: What is a Sloop?
With just one mast and a fore-and-aft rig, sloops are known for their simplicity and versatility. These characteristics make them an excellent choice for sailors of all levels. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, you’ll find that the design of a sloop allows for easy handling and maneuverability.
The single mast on a sloop is typically located towards the front of the boat. This placement provides several advantages when sailing upwind, the sail can be adjusted easily to maintain an optimal angle with respect to the wind. This is because there is only one sail to worry about, unlike other types of boats that may have multiple sails.
Similarly, when sailing downwind, a sloop’s sail can be adjusted quickly to take advantage of any changes in wind direction or speed. This flexibility makes it possible to navigate challenging weather conditions with ease.
External Links, See Also
For those looking for more technical information on sloops and other types of sailboats, the Boatdesign.net forum is an excellent resource. Here you can find discussions on everything from mast design to hull construction.
Finally, if you’re looking for some great books on sailing and sailboat design, be sure to check out “The Elements of Seamanship” by Roger C. Taylor or “Sailing Alone Around the World” by Joshua Slocum.







